What does melanoma look like, and where can it be found on the body?
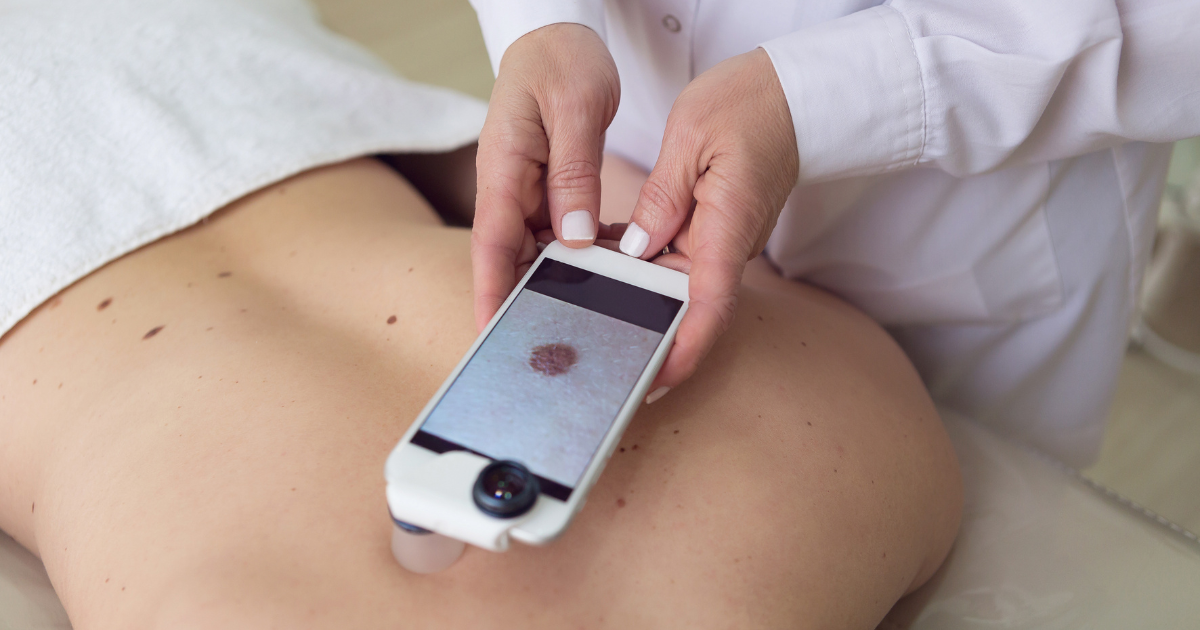
Melanoma is a type of cancer that originates from cells that produce the pigment responsible for our skin color. Understanding what melanoma looks like and where it can be found on the body can help with early diagnosis and treatment.
“Although it’s not the most common type of skin cancer, melanoma can be a more deadly form of skin cancer if not diagnosed and treated in an early stage,” says double board-certified dermatologist and Mohs surgeon Adam Sutton, MD. “That’s why it’s so important to know where melanoma can develop and its risk factors.”
Understanding melanoma and its risk factors
Melanoma is primarily caused by the abnormal growth of cells called melanocytes, which can lead to the formation of cancerous lesions on the skin. While anyone can develop melanoma, certain factors can increase the risk. These include:
- History of indoor tanning: Excessive exposure to artificial UV radiation, such as tanning beds, increases the risk of developing melanoma.
- Family history: If you have a family member who has been diagnosed with melanoma, your risk may be higher.
- Fair skin, blue eyes or red hair: People with fair skin, blue eyes, or red hair are more susceptible to melanoma due to their reduced ability to produce melanin, which provides natural protection against UV radiation.
- Living near the equator: Regions closer to the equator receive more intense sunlight, which can increase the risk of developing melanoma.
- Higher mole count: Individuals with more moles are at higher risk for the development of melanoma.
What are the signs and symptoms of melanoma?
To identify potential signs of melanoma, it is important to remember the ABCDE rule:
A - Asymmetry: One half of the mole or spot does not match the other half.
B - Border: The edges of the mole are irregular, blurred or jagged.
C - Color: The color of the mole is not uniform and may include different shades of brown or black.
D - Diameter: Melanomas are often larger in diameter than a pencil eraser.
E - Evolving: The mole or spot changes in size, shape or color or exhibits other symptoms such as itching, bleeding or crusting.
Where is melanoma found on the body?
The most common locations of melanoma on the body can vary with age and gender. In younger males, melanoma is commonly found on the back or chest. Younger women often develop melanoma on their legs.
For individuals in their 60s and older, melanoma is most often found on chronically sun-exposed areas such as the head and neck. This highlights the importance of protecting these areas from excessive sun exposure.
Despite these general rules, melanoma can occur anywhere on the body where there are melanocytes. These areas include skin, nails, eye and gastrointestinal tract.
The importance of self-examination and seeing a dermatologist
Regular self-examination of the skin is important for early detection of melanoma. Use mirrors or involve a significant other to thoroughly examine areas that are hard to see. Pay close attention to any new, changing, bleeding or growing moles or spots on your skin.
If you have concerns about your skin or have risk factors for melanoma, it is best to schedule a full-body skin check or skin cancer screening with a board-certified dermatologist. During this visit, the provider will use special lights and instruments to examine the skin from the scalp to the tip of the toes, looking for suspicious or changing spots.
Prevention and early diagnosis
Prevention is critical in reducing the risk of melanoma. Protect yourself from the sun by:
- Wearing a broad-spectrum sunscreen with at least SPF 30 and reapply it every two hours.
- Seeking shade and avoiding the sun during peak UV hours, typically between 10 a.m. and 4 p.m.
- Wearing UV-protective clothing that covers your skin.
- Remembering that UV rays can penetrate glass windows and, even on cloudy days, the UV index can be as high as 80% of what it is on a sunny day.
Early diagnosis plays a crucial role in the successful treatment of melanoma, according to Dr. Sutton.
“When it’s diagnosed early, melanoma is highly curable, so if you’re going to have melanoma, we like to have an early melanoma,” he says. “Skin exams by a board-certified dermatologist can help identify melanoma at an earlier stage.”
The Nebraska Medicine comprehensive skin cancer program works with patients with all forms of melanoma and nonmelanoma skin cancers, as well as suspected cases. The skin cancer team includes experts from multiple disciplines who treat and manage skin cancer patients.







